شركة Shining Aluminium Packaging هي شركة رائدة في توريد أسطوانات الغاز عالية الضغط في الصين. لقد تبرعنا بأنفسنا للبحث والتطوير في مجال الأسطوانات منذ عام 2001، بهدف توفير منتجات عالية الجودة لصناعات المشروبات والغوص والطب والسلامة من الحرائق والصناعات الخاصة.
مصنع اسطوانة غاز الالمنيوم
معدات
يتم ضمان مراقبة الجودة لدينا من خلال التوافق الصارم مع المعايير الدولية بما في ذلك ISO و DOT و TPED، ونحن مجهزون بآلات أوتوماتيكية متقدمة وأنظمة إنتاج بموجب ISO9001 لتلبية أو تجاوز متطلبات وتوقعات عملائنا والمعايير الدولية.
الشهادات - التوصيات
نظرًا لأننا نقدر حقًا خدمتك وجودة منتجاتك للطباعة والألمنيوم الجيدة جدًا ، فإننا نفكر فيك كمورد مرجعي لنا في أي مشروع جديد يحتوي على عبوات ألمنيوم.
وفاء حلوم المسؤول عن المشروع
لقد كنت شريكًا رائعًا لنا ونأمل أن تتفهم حاجتنا إلى مزيد من المرونة خلال هذا الوقت غير المعتاد.
كريس ثوسجع
سابق
التالي
ابحث عن اسطوانات الغاز الألومنيوم؟
الدليل الشامل لأسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم
1 المقدمة
1.1 تعريف أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم
أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم عبارة عن حاوية مصنوعة من الألومنيوم 6061 مصممة لتخزين ونقل الغازات المضغوطة مثل الأكسجين والنيتروجين والهيليوم وثاني أكسيد الكربون. تُستخدم هذه الأسطوانات عادةً في تطبيقات صناعية وطبية مختلفة حيث تكون هناك حاجة إلى مصدر غاز مضغوط محمول وخفيف الوزن.
تتمتع أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم بالعديد من المزايا مقارنة بالأسطوانات الفولاذية، بما في ذلك خفة الوزن، مما يجعلها أكثر قابلية للحمل، ومقاومة أفضل للتآكل، مما قد يساعد في إطالة عمرها الافتراضي. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، تتمتع أسطوانات الألومنيوم بموصلية حرارية أعلى، مما يسمح بتبديد الحرارة بكفاءة أكبر أثناء تعبئة الغاز وتفريغه. ومع ذلك، قد تكون أسطوانات الألومنيوم أكثر تكلفة من أسطوانات الفولاذ بسبب التكلفة الأعلى للمواد المستخدمة في تصنيعها.
1.2 تاريخ أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم
يعود تاريخ أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم إلى أوائل القرن العشرين، عندما تم اكتشاف الألومنيوم لأول مرة باعتباره مادة مناسبة للاستخدام في بناء حاويات الضغط العالي. قبل استخدام الألومنيوم، كانت أسطوانات الغاز مصنوعة عادةً من الفولاذ أو الحديد، والتي كانت ثقيلة وعرضة للصدأ.
في عشرينيات القرن العشرين، بدأت شركة مانسمان الألمانية في إنتاج أسطوانات غاز من الألومنيوم لصناعة الطيران الناشئة. استُخدمت هذه الأسطوانات في البداية لتخزين الهواء المضغوط في أنظمة الطائرات الهوائية. كانت أخف وزنًا من نظيراتها المصنوعة من الفولاذ، مما يجعلها مثالية للاستخدام في الطائرات حيث كان الوزن عاملاً حاسمًا.
بدأ استخدام أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم على نطاق واسع في أربعينيات وخمسينيات القرن العشرين في تطبيقات مختلفة، بما في ذلك اللحام والغوص وتخزين الأكسجين الطبي. كانت هذه الأسطوانات تُصنع عادةً باستخدام عملية بثق سلسة تنتج حاوية خفيفة الوزن وعالية القوة.
مع مرور الوقت، تطور تصميم أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم، مع التحسينات في المواد وعمليات التصنيع ومعايير السلامة. واليوم، تُستخدم أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم في تطبيقات مختلفة، بما في ذلك في القطاعات الطبية والصناعية والترفيهية. وهي ذات قيمة لخفة وزنها ومتانتها ومقاومتها للتآكل، وهي مكون أساسي في العديد من التقنيات الحديثة.
1.3 فوائد أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم
هناك العديد من الفوائد لاستخدام أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم، بما في ذلك:
- خفيفة الوزن: تعتبر أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم أخف وزنًا من الأسطوانات المصنوعة من الفولاذ، مما يجعلها أسهل في التعامل والنقل.
- مقاومة للتآكل: تتميز أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم بمقاومتها للتآكل، مما يجعلها أكثر متانة وأطول عمراً.
- قوة عالية: يعتبر غاز الألومنيوم مادة قوية ومتينة يمكنها تحمل الضغوط العالية، مما يجعله مثاليًا لأسطوانات الغاز.
- غير مغناطيسية: أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم غير مغناطيسية، مما يجعلها أكثر أمانًا للاستخدام في البيئات التي تشكل فيها المجالات المغناطيسية مصدر قلق.
- نقاء غاز عالي: تتمتع أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم بمستوى عالٍ من نقاء الغاز، وهو أمر ضروري للتطبيقات التي تتطلب مستوى عالٍ من نقاء الغاز، مثل التطبيقات الطبية والعلمية.
- قابل لإعادة التدوير: يعد الألومنيوم مادة قابلة لإعادة التدوير بدرجة كبيرة، وإعادة تدوير الألومنيوم يوفر 95% من الطاقة اللازمة لإنتاجه من المواد الخام. وهذا يعني أنه يمكن إعادة تدوير أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم بشكل متكرر، مما يقلل من النفايات ويحافظ على الموارد الطبيعية.
2. هيكل أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم
تُصنع أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم عادةً من سبائك الألومنيوم عالية القوة التي توفر بنية خفيفة الوزن ومتينة. قد يختلف التصميم المحدد للأسطوانة حسب الاستخدام المقصود، ولكن معظم أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم لها بنية أساسية مماثلة.
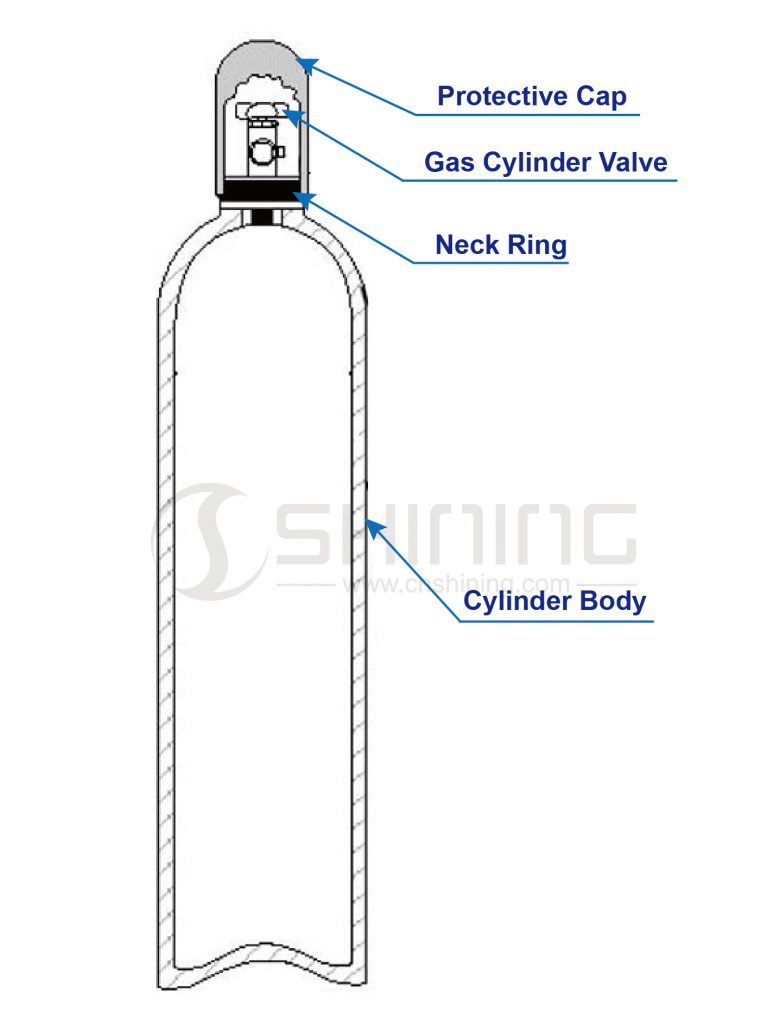
المكونات الرئيسية لأسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم تشمل:
جسم الاسطوانة: هذا هو الجزء الرئيسي من الأسطوانة وهو أسطواني الشكل عادةً. يتكون الجسم من أنبوب من سبائك الألومنيوم المبثوق بدون درزات مصمم لتحمل الضغط العالي. يحدد تصنيف ضغط الأسطوانة سمك جدران الأسطوانة.
حلقة العنق: هذا طوق في الجزء العلوي من جسم الأسطوانة. توفر حلقة العنق نقطة تثبيت آمنة للصمام وتحمي الأسطوانة من التلف أثناء المناولة والنقل. عادة ما يتم تثبيت حلقات العنق بالمسامير بدلاً من الخيوط لأن الخيوط ستقلل من سمك جدار أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم.
صمام أسطوانة الغاز: صمام أسطوانة الغاز هو جهاز يتحكم في تدفق الغاز داخل وخارج أسطوانة الغاز. وعادة ما يكون مصنوعًا من النحاس أو الفولاذ ومصممًا ليكون متينًا ومقاومًا للضغط العالي. وعادة ما يكون الصمام متصلاً بأسطوانة الألومنيوم باستخدام وصلة ملولبة، ويمكن فتحه أو إغلاقه باستخدام عجلة صمام أو مقبض. تم تصميم صمامات أسطوانة الغاز لتكون آمنة وموثوقة، وعادة ما تحتوي على بعض ميزات الأمان المدمجة. على سبيل المثال، تحتوي العديد من الصمامات على جهاز تخفيف الضغط الذي سيخرج الغاز تلقائيًا إذا تجاوز الضغط داخل الأسطوانة مستوى معينًا. يساعد هذا في منع الأسطوانة من الانفجار أو التمزق.
غطاء الحماية: الغطاء الواقي هو غطاء بلاستيكي أو معدني يوضع فوق الصمام لحمايته من التلف والتلوث عندما لا تكون الأسطوانة قيد الاستخدام.
بشكل عام، يركز تصميم أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم على توفير هيكل قوي وخفيف الوزن ومتين يمكنه احتواء الغازات عالية الضغط بأمان. تعتمد المكونات والميزات المحددة للأسطوانة على الاستخدام المقصود ومتطلبات التطبيق.
3. علامات أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم
يجب وضع علامات على أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم وفقًا للقواعد التي وضعتها وزارة النقل (DOT) ووزارة النقل الكندية (TC). توفر العلامات معلومات أساسية حول محتويات الأسطوانة واستخدامها وسلامتها.
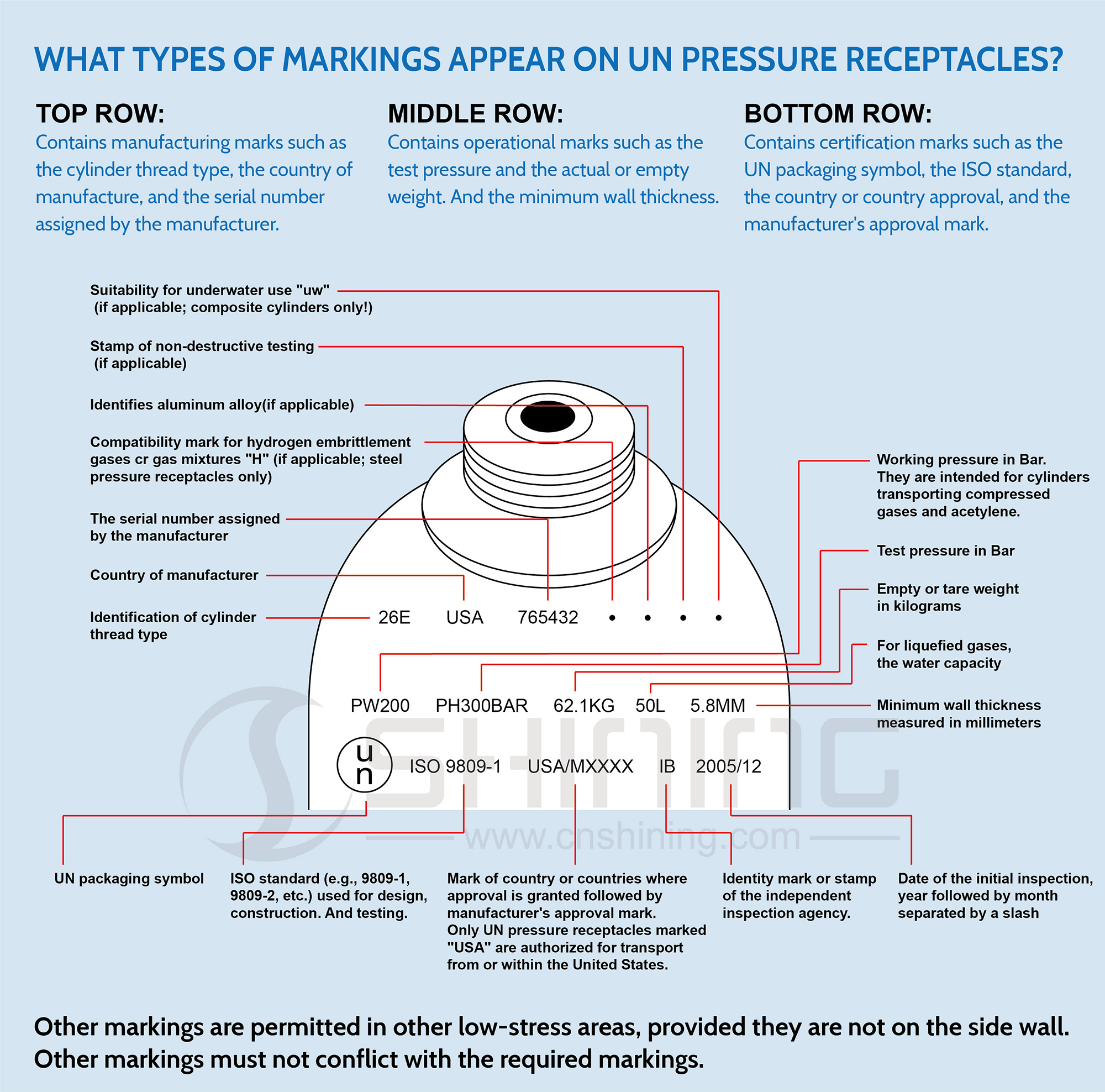
فيما يلي بعض العلامات القياسية التي قد تراها على أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم:
الصف العلوي:تحتوي على علامات التصنيع مثل نوع خيط الأسطوانة، وبلد التصنيع، والرقم التسلسلي المخصص من قبل الشركة المصنعة.
- ملائمة للاستخدام تحت الماء "uw" إذا كان ذلك ممكنًا؛ الأسطوانات المركبة فقط!
- ختم الاختبار غير المدمر (إن وجد)
- يحدد سبيكة الألومنيوم (إن وجدت).
- علامة التوافق لغازات الهشاشة الهيدروجينية مخاليط الغازات "H" (إذا كان ذلك ممكنًا؛ أوعية الضغط الفولاذية فقط)
- الرقم التسلسلي المخصص من قبل الشركة المصنعة
- بلد المنشأ
- تحديد نوع خيط الأسطوانة
الصف الأوسط: يحتوي على علامات التشغيل مثل ضغط الاختبار والوزن الفعلي أو الفارغ والحد الأدنى لسمك الجدار.
- ضغط العمل بالبار. وهي مخصصة للأسطوانات التي تنقل الغازات المضغوطة والأسيتيلين.
- اختبار الضغط بالبار
- الوزن فارغًا أو فارغًا بالكيلوجرام
- بالنسبة للغازات المسالة، سعة المياه
- الحد الأدنى لسمك الجدار يقاس بالملليمتر
الصف السفلي: تحتوي على علامات التصديق مثل رمز التغليف الخاص بالأمم المتحدة، ومعيار ISO، والدولة أو موافقة الدولة، وعلامة موافقة الشركة المصنعة.
- رمز التعبئة للأمم المتحدة
- معيار ISO (على سبيل المثال، 9809-1، 9809-2، وما إلى ذلك) المستخدم في التصميم والبناء والاختبار.
- علامة الدولة أو الدول التي تم منح الموافقة عليها تليها علامة موافقة الشركة المصنعة. لا يُسمح بنقل أوعية الضغط التابعة للأمم المتحدة التي تحمل علامة "USA" إلا من الولايات المتحدة أو داخلها.
- علامة هوية أو ختم وكالة التفتيش المستقلة.
- تاريخ الفحص الأولي، السنة متبوعة بالشهر مفصولة بعلامة مائلة
4. أنواع الأسطوانات ذات الضغط العالي حسب المادة
الأسطوانات الفولاذية، والأسطوانات المصنوعة من الألومنيوم، والأسطوانات المركبة هي أسطوانات مختلفة عالية الضغط تستخدم لتخزين ونقل الغازات المختلفة.
اسطوانات فولاذية تعتبر الأسطوانات الفولاذية أكثر أنواع أسطوانات الغاز شيوعًا، وعادةً ما تكون مصنوعة من الفولاذ الكربوني المسحوب بدون درزات. وهي متينة ويمكنها تحمل الضغوط العالية، مما يجعلها مناسبة لتخزين ونقل مجموعة واسعة من الغازات. كما أن الأسطوانات الفولاذية غير مكلفة نسبيًا ويمكن إعادة استخدامها عدة مرات. ومع ذلك، فهي ثقيلة ويمكن أن تكون عرضة للتآكل إذا لم يتم صيانتها بشكل صحيح.
اسطوانات الالمنيوم تعتبر الأسطوانات المصنوعة من الألومنيوم بديلاً أخف وزناً للأسطوانات الفولاذية. فهي مصنوعة من سبائك الألومنيوم عالية القوة وهي أكثر مقاومة للتآكل من الأسطوانات الفولاذية. كما أن الأسطوانات المصنوعة من الألومنيوم أغلى ثمناً من الأسطوانات الفولاذية، ولكن خصائصها خفيفة الوزن ومقاومة التآكل تجعلها شائعة في تطبيقات محددة، مثل الغوص والأكسجين الطبي.
اسطوانة من ألياف الكربون المركبة تعتمد على أسطوانة داخلية من سبائك الألومنيوم ذات جدار رقيق ومغلفة بمادة مركبة من ألياف الكربون. وهي أخف وزنًا من الأسطوانات المصنوعة من الفولاذ والألومنيوم وتتمتع بقوة ومتانة ممتازتين. كما تتمتع الأسطوانات المركبة بمقاومة عالية للتآكل ويمكنها تخزين مجموعة واسعة من الغازات، بما في ذلك الأكسجين والنيتروجين وثاني أكسيد الكربون. ومع ذلك، فهي أكثر تكلفة من الأسطوانات المصنوعة من الفولاذ والألومنيوم.
باختصار، كل نوع من الأسطوانات له مميزاته وعيوبه الفريدة، ويعتمد اختيار النوع الذي يجب استخدامه على متطلبات التطبيق المحددة.
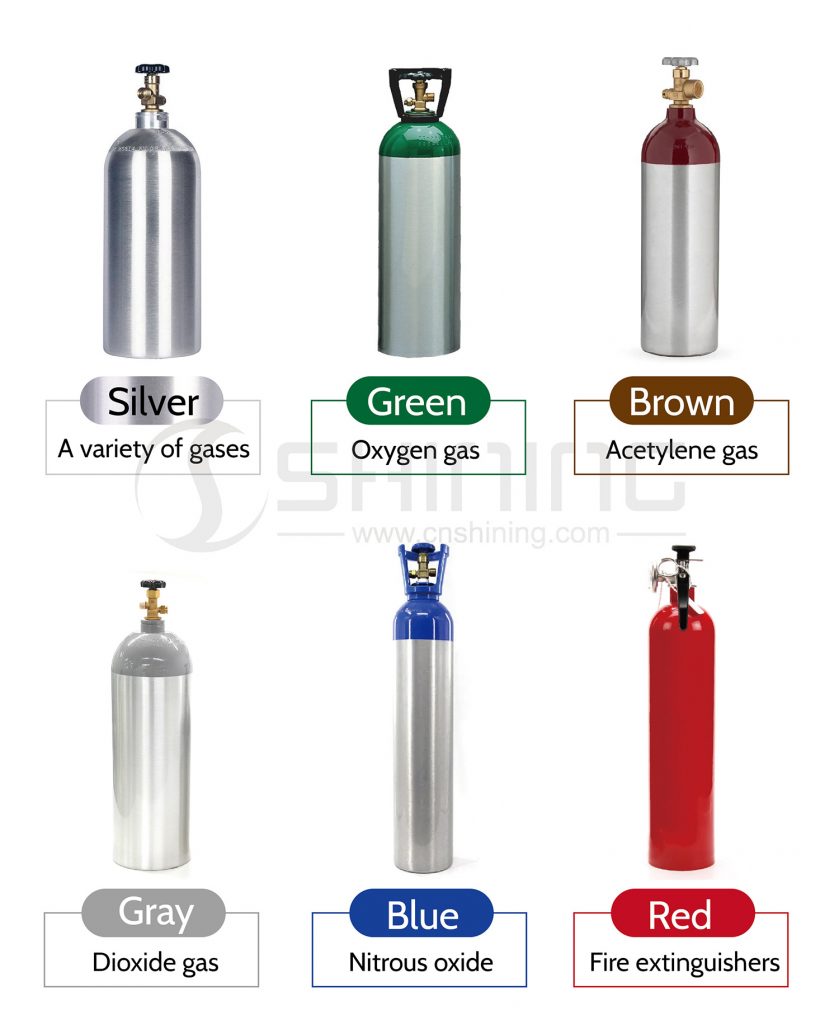
5. لون أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم
يمكن أن تأتي أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم بألوان مختلفة حسب الاستخدام المقصود أو الصناعة. اللون الأكثر شيوعًا لأسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم هو اللون الفضي، وهو اللون الطبيعي للمعدن. ومع ذلك، قد يطبق المصنعون أيضًا ألوانًا مختلفة على الأسطوانات باستخدام الطلاء أو الطلاء المسحوق لأغراض التعريف أو السلامة.
غالبًا ما يتم توحيد ترميز الألوان لأسطوانات الغاز وفقًا لمعايير الصناعة لضمان التعامل الآمن والتخزين والنقل. على سبيل المثال، في الولايات المتحدة، أنشأت جمعية الغاز المضغوط (CGA) نظام ترميز الألوان لعلامات كتف أسطوانات الغاز وأغطية حماية الصمامات. يستخدم هذا النظام ألوانًا محددة للإشارة إلى نوع الغاز ومستوى خطورته وغير ذلك من المعلومات المهمة.
- فضي: اللون الأكثر شيوعًا لأسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم هو اللون الفضي، وهو اللون الطبيعي للمعدن. يمكن استخدام هذه الأسطوانات لغازات مختلفة ولا يتم تخصيصها عادةً لأي نوع محدد من الغاز.
- أخضر: تُستخدم الأسطوانات الخضراء غالبًا لغاز الأكسجين، لأن الأكسجين ضروري لحياة النبات، ويرتبط اللون الأخضر بالطبيعة والنمو.
- بني: تُستخدم الأسطوانات ذات اللون البني عادةً لغاز الأسيتيلين، والذي يُستخدم عادةً في تطبيقات اللحام والقطع. ويُستخدم هذا اللون أحيانًا أيضًا للغازات القابلة للاشتعال الأخرى.
- رمادي: تُستخدم الأسطوانات الرمادية عادةً لغاز ثاني أكسيد الكربون، والذي يُستخدم عادةً في تطبيقات الأغذية والمشروبات، مثل صودا الخبز والبيرة.
- أزرق: تُستخدم الأسطوانات الزرقاء غالبًا لأكسيد النيتروز. ويُستخدم هذا اللون أحيانًا أيضًا للغازات غير القابلة للاشتعال الأخرى.
- أحمر: تُستخدم الأسطوانات الحمراء غالبًا في أجهزة إطفاء الحرائق، التي تحتوي على غازات مضغوطة تُستخدم لإطفاء الحرائق. ويُستخدم هذا اللون أحيانًا أيضًا في أنواع أخرى من الغازات المضغوطة.
من المهم ملاحظة أن لون الأسطوانة قد يختلف حسب الشركة المصنعة وأن نظام ترميز الألوان المستخدم لتحديد الغازات قد يختلف حسب المنطقة أو البلد. لذلك، من الضروري دائمًا الرجوع إلى ملصق الأسطوانة أو استشارة متخصص مدرب لضمان تحديد أسطوانات الغاز بشكل صحيح.
6. نوع محول تركيب صمام أسطوانة الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم
CGA (جمعية الغاز المضغوط) وDIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) هما معياران لتركيبات أسطوانات الغاز.
المعيار الأمريكي: CGA
تُستخدم تجهيزات CGA بشكل شائع في أمريكا الشمالية ويتم تحديدها بنظام رقمي (على سبيل المثال، CGA 320، CGA 580). تتمتع هذه التجهيزات بأبعاد وخيوط محددة مصممة للتوصيل بصمام أسطوانة الغاز المناسب. تتضمن بعض تجهيزات CGA القياسية ما يلي:
- CGA 320: يستخدم لثاني أكسيد الكربون والغازات الخاملة الأخرى
- CGA 580: يستخدم للهواء المضغوط والنيتروجين
- CGA 540: يستخدم للأكسجين
- CGA 870: يستخدم للأكسجين الطبي
- CGA 510: يستخدم للأسيتيلين
- CGA 590: يستخدم للأرجون
- CGA 180: يستخدم للهيليوم
- CGA 200: يستخدم للنيتروجين
- CGA 326: يستخدم لأكسيد النيتروز
المعيار الأوروبي: DIN 477
تُستخدم تجهيزات DIN بشكل شائع في أوروبا ويتم تحديدها من خلال رقم DIN (على سبيل المثال، DIN 477-1، DIN 477-5). تتمتع هذه التجهيزات أيضًا بأبعاد وخيوط محددة مصممة للتوصيل بصمام أسطوانة الغاز المناسب. تتضمن بعض تجهيزات DIN القياسية ما يلي:
- DIN 477-1: يستخدم للنيتروجين والأرجون
- DIN 477-5: يستخدم لثاني أكسيد الكربون
- DIN 477-6: يستخدم للأكسجين
- DIN 477-7: يستخدم للبروبان والبوتان
- DIN 477-8: يستخدم للهيدروجين
- DIN 477-9: يستخدم للهيليوم
- DIN 477-10: يستخدم للأسيتيلين
إذا كنت بحاجة إلى توصيل أسطوانة غاز بتركيبة CGA بنظام يتطلب تركيب DIN (أو العكس)، فيمكنك استخدام محول التركيب. تتوفر محولات DIN لتركيبات CGA المختلفة، كما تتوفر محولات CGA لتركيبات DIN المختلفة.
المعيار البريطاني:BS341
تحدد المواصفة القياسية البريطانية لوصلات صمامات أسطوانات الغاز BS341 الأنواع المختلفة من وصلات الصمامات المستخدمة في أسطوانات الغاز. وفيما يلي الأنواع المختلفة من الوصلات التي حددتها المواصفة BS341:
- BS 341 رقم 2 - يستخدم هذا الاتصال لغازات البوتان والبروبان ويعرف أيضًا باسم صمام 21.7 مم.
- BS 341 رقم 3 - يستخدم هذا الاتصال للغاز البترولي المسال (LPG) ويعرف أيضًا باسم صمام 25 مم.
- BS 341 رقم 4 - يستخدم هذا الاتصال لغاز الأسيتيلين ويعرف أيضًا باسم صمام 9/16 بوصة.
- BS 341 رقم 6 - تستخدم هذه الوصلة لغاز الأكسجين المعروف أيضًا باسم الصمام 3/4 بوصة.
- BS 341 رقم 8 - يستخدم هذا التوصيل لغاز ثاني أكسيد الكربون، المعروف أيضًا باسم الصمام 5/8 بوصة.
- BS 341 رقم 10 – يستخدم هذا الوصل لغاز النيتروجين ويعرف أيضًا بالصمام 1 1/8″.
- BS 341 رقم 13 - تستخدم هذه الوصلة لغاز الأرجون، المعروف أيضًا باسم الصمام 5/8 بوصة.
منافذ وتوصيلات صمامات الأسطوانة
أسطوانات الغاز ذات الصمامات ذات وصلات مخرج قياسية BS وCGA وDIN. في بعض الحالات يمكن استخدام وصلات بديلة وسيتم توفيرها بناء على طلب العميل بدلاً من المواصفات الموضحة أدناه.
| غاز | بكالوريوس | سي جي ايه | الدين | غاز | بكالوريوس | سي جي ايه | الدين |
| الأسيتيلين | 2 | 510 | - | كلوريد الهيدروجين | 6 | 330 | 8 |
| هواء | 3 | 590 | 6 | كبريتيد الهيدروجين | 15 | 330 | 5 |
| ألين | - | 510 | 1 | ايزو البيوتان | 4 | 510 | 1 |
| الأمونيا، اللامائية | 10 | 240, 660 | 8 | ايزو بوتيلين | 4 | 510 | 1 |
| الأرجون | 3 | 580 | 10 | كريبتون | 3 | 580 | 10 |
| أرسين | 4 | 350 | 5 | الميثان | 4 | 350 | 1 |
| 1،3-بوتادين | 4 | 510 | 1 | كلوريد الميثيل | 7 | 660 | 5 |
| البيوتان | 4 | 510 | 1 | ميثيل مركابتان | - | 330 | 5 |
| بوتينيس | 4 | 510 | 1 | أحادي إيثيل أمين | 11 | 240 | 5 |
| ثاني أكسيد الكربون | 8 | 320 | 6 | مونوميثيلامين | 11 | 240 | 5 |
| أول أكسيد الكربون | 4 | 350 | 5 | غاز طبيعي | 4 | 350 | 1 |
| فلوريد الكربونيل | - | 660 | 8 | نيون | 3 | 580 | 10 |
| كبريتيد الكربونيل | - | 330 | 5 | أكسيد النيتريك | 14 | 660 | 8 |
| الكلور | 6 | 660 | 8 | نتروجين | 3 | 580 | 10 |
| سيانوجين | - | 660 | 8 | ثاني أكسيد النيتروجين | 14 | 660 | 8 |
| الديوتيريوم | 4 | 350 | 1 | أكسيد النيتروز | 13 | 326 | 6 |
| ديميثيلامين | 11 | 240 | 5 | الأكسجين | 3 | 540 | - |
| الأثير ثنائي ميثيل | - | 510 | 1 | الفوسجين | 6 | 660 | 8 |
| الإيثان | 4 | 350 | 1 | الفوسفين | 4 | 350 | 5 |
| إيثيل الأسيتيلين | - | 510 | 1 | البروبان | 4 | 510 | 1 |
| كلوريد الإيثيل | 7 | 510 | 1 | البروبيلين | 4 | 510 | 1 |
| الإيثيلين | 4 | 350 | 1 | سيلاني | - | 350 | 5 |
| أكسيد الإثيلين | 7 | 510 | 1 | رباعي فلوريد السيليكون | - | 330 | 8 |
| هالوكربون 14 | 6 | 580 | 6 | ثاني أكسيد الكبريت | 12 | 660 | 8 |
| هالوكربون 22 | 6 | 660 | 6 | سادس فلوريد الكبريت | 6 | 590 | 6 |
| الهيليوم | 3 | 580 | 10 | تريميثيلامين | 11 | 240 | 5 |
| هيدروجين | 4 | 350 | 1 | كلوريد الفينيل | 7 | 510 | 5 |
| بروميد الهيدروجين | - | 330 | 8 | زينون | 3 | 580 | 10 |
| كلوريد الهيدروجين | 6 | 330 | 8 |
7. تصنيع أسطوانات غاز الألمنيوم
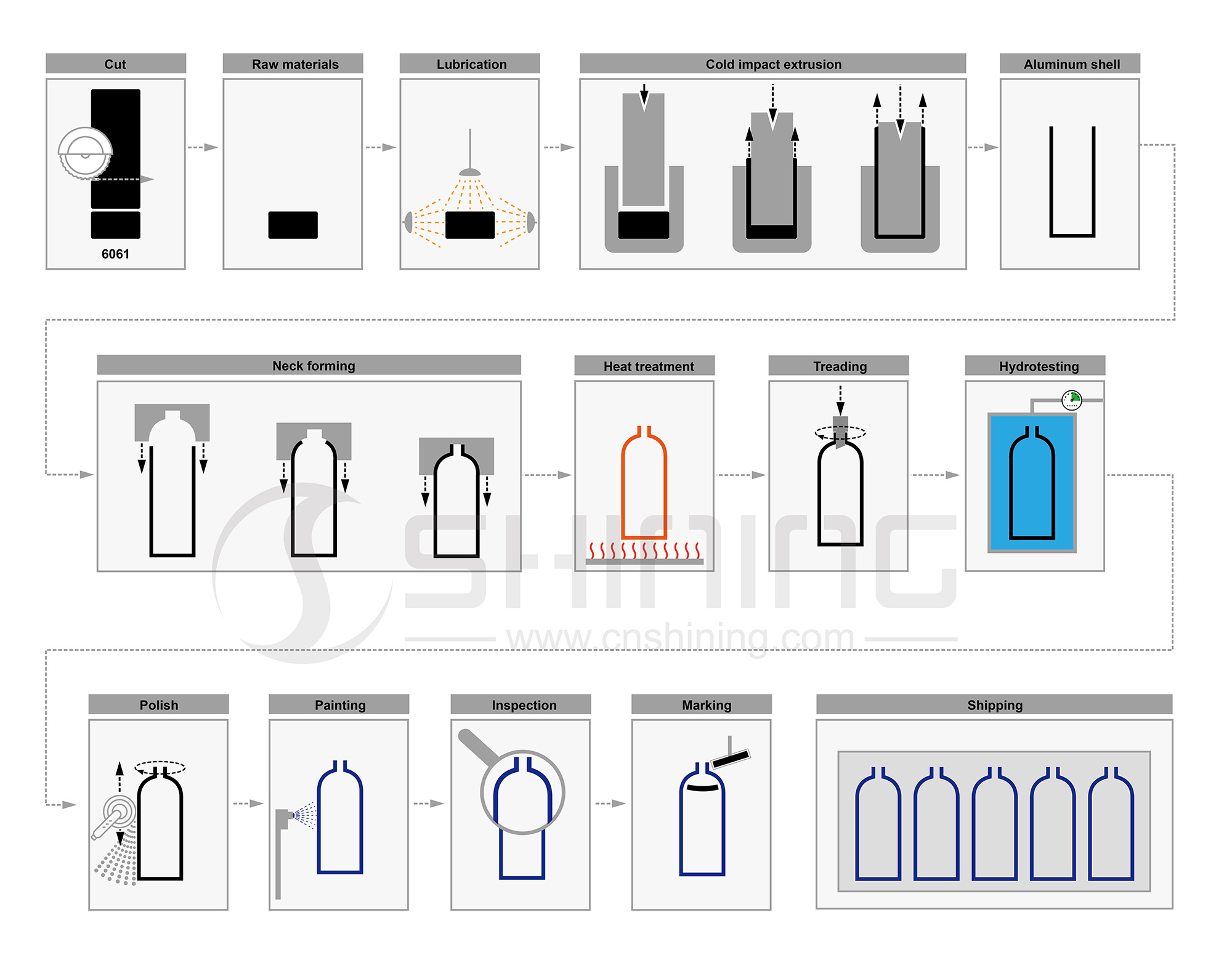
فيما يلي نظرة عامة على الخطوات المتبعة في عملية تصنيع أسطوانة غاز الألومنيوم:
مواد خام: المادة الخام الأولية المستخدمة في تصنيع أسطوانة غاز الألمنيوم هي سبيكة ألومنيوم مصنوعة من 6061 سبيكة. البزاقة عبارة عن قطعة أسطوانية من المعدن ستشكل في النهاية جسم الأسطوانة.
تشحيم: يتم تشحيم البزاقة لتقليل الاحتكاك أثناء عملية التصنيع. هذا يساعد على منع البزاقة من الالتصاق بالقالب أثناء البثق.
قذف التأثير البارد: ثم يتم وضع البزاقة المشحمة في قالب وتخضع لقذف الصدمة الباردة. تتضمن هذه العملية ضغط البزاقة تحت ضغط عالٍ لتشكيل غلاف أسطواني.
تشكيل العنق: بعد تشكيل الغلاف ، يتم تشكيل الطرف العلوي وتشكيله لإنشاء رقبة حيث سيتم توصيل الصمام.
المعالجة الحرارية: ثم تخضع القشرة للمعالجة الحرارية ، والتي تتضمن التبريد لزيادة قوتها وصلابتها. ثم يتم تقادم عمر القشرة في فرن معالجة بمحلول T6 للحصول على القوة والمتانة المطلوبة.
الدوس: الغلاف مسنن على الطرف العلوي للسماح بربط الصمام.
الاختبار المائي: تخضع الأسطوانة بعد ذلك للاختبار الهيدروستاتيكي ، حيث يتم ملؤها بالماء وضغطها لضمان قدرتها على تحمل الضغط المطلوب.
تلميع: يتم بعد ذلك صقل الأسطوانة لإزالة أي عيوب سطحية ولإنشاء سطح أملس.
تلوين: الأسطوانة مطلية بطلاء متين لحمايتها من التآكل ولجعلها أكثر جاذبية من الناحية المرئية.
تقتيش: يتم فحص الأسطوانة للتأكد من أنها تلبي جميع المواصفات والمعايير المطلوبة.
العلامات: يتم تمييز الأسطوانة برموز مختلفة، بما في ذلك اسم الشركة المصنعة والرقم التسلسلي وعلامات التعريف الأخرى.
شحن: أخيرًا ، يتم تغليف الأسطوانات وشحنها للعملاء الذين طلبوها.
هذه نظرة عامة على عملية التصنيع ، وقد تختلف التفاصيل المحددة اعتمادًا على الشركة المصنعة والاستخدام المقصود للأسطوانة.
8. اختبار واعتماد اسطوانة الغاز
يختلف اختبار واعتماد أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم حسب الدولة ، حيث أن لكل دولة لوائحها ومعاييرها. فيما يلي بعض الأمثلة على اختبار واعتماد أسطوانة غاز الألومنيوم في بلدان مختلفة:
الولايات المتحدة: في الولايات المتحدة، يتم تنظيم أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم من قبل وزارة النقل (DOT). يجب اختبار الأسطوانات واعتمادها من قبل منشأة معتمدة من وزارة النقل كل 5 سنوات باستخدام طرق محددة، بما في ذلك الاختبار الهيدروستاتيكي والموجات فوق الصوتية. يجب أن تحمل الأسطوانات أيضًا علامات محددة، بما في ذلك علامة مواصفات DOT، واسم الشركة المصنعة وعنوانها، والرقم التسلسلي للأسطوانة.
كندا: في كندا، يتم تنظيم أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم بواسطة هيئة النقل الكندية. يجب اختبار الأسطوانات واعتمادها كل 10 سنوات بواسطة منشأة معتمدة من TC باستخدام طرق اختبار محددة، بما في ذلك الاختبار الهيدروستاتيكي والفحص البصري. ويجب أن تحمل الأسطوانات أيضًا علامات محددة، بما في ذلك علامة مواصفات TC، واسم الشركة المصنعة وعنوانها، والرقم التسلسلي للأسطوانة.
المملكة المتحدة: في المملكة المتحدة، يتم تنظيم أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم من قبل هيئة الصحة والسلامة التنفيذية (HSE). يجب اختبار الأسطوانات واعتمادها كل 5 أو 10 سنوات، اعتمادًا على استخدامها، من قبل منشأة معتمدة من قبل الصحة والسلامة والبيئة باستخدام طرق اختبار محددة، بما في ذلك الاختبار الهيدروستاتيكي والفحص البصري. يجب أن تحمل الأسطوانات أيضًا علامات محددة، بما في ذلك علامة مواصفات EN، واسم الشركة المصنعة وعنوانها، والرقم التسلسلي للأسطوانة.
الاتحاد الأوروبي: في الاتحاد الأوروبي، يجب أن تتوافق أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم مع توجيهات معدات الضغط (PED) وتوجيهات معدات الضغط القابلة للنقل (TPED). توفر هذه التوجيهات إطارًا لاختبار وإصدار الشهادات لأسطوانات الغاز، بما في ذلك أسطوانات الألومنيوم. ويجب أن يتم اختبار الأسطوانات واعتمادها من قبل هيئة معتمدة كل 10 سنوات باستخدام طرق اختبار محددة، بما في ذلك الاختبار الهيدروستاتيكي والاختبار بالموجات فوق الصوتية. ويجب أن تحمل الأسطوانات أيضًا علامات محددة، بما في ذلك علامة CE واسم الشركة المصنعة وعنوانها والرقم التسلسلي للأسطوانة.
أستراليا: في أستراليا، يتم تنظيم أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم من قبل جمعية الغاز الأسترالية (AGA). ويجب اختبار الأسطوانات واعتمادها كل 10 سنوات من قبل منشأة معتمدة من قبل AGA باستخدام طرق اختبار محددة، بما في ذلك الاختبار الهيدروستاتيكي والفحص البصري. يجب أن تحمل الأسطوانات أيضًا علامات محددة، بما في ذلك علامة مواصفات AGA واسم الشركة المصنعة وعنوانها والرقم التسلسلي للأسطوانة.
من المهم ملاحظة أن هذه اللوائح والمعايير قد تتغير بمرور الوقت ويمكن أن تختلف اعتمادًا على نوع أسطوانة الغاز والاستخدام المقصود منها. لذلك، من الأفضل دائمًا استشارة هيئة مهنية أو تنظيمية مؤهلة للتأكد من أن أسطوانة غاز الألومنيوم الخاصة بك تلبي متطلبات الاختبار والاعتماد المناسبة في بلدك.
9. تطبيقات اسطوانة غاز الألومنيوم
هناك عدة أنواع من أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم المستخدمة في تطبيقات مختلفة:
- اسطوانات SCBA (جهاز التنفس الذاتي): يتم استخدام أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم من قبل رجال الإطفاء وعمال الإنقاذ والعاملين في الصناعة الذين يحتاجون إلى حماية الجهاز التنفسي في البيئات الخطرة.
- الاسطوانات الصناعية واللحام: تُستخدم أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم في صناعات مثل التصنيع والبناء وتشغيل المعادن من أجل اللحام والقطع والعمليات الصناعية الأخرى.
- الاسطوانات الطبية: تُستخدم أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم هذه في أماكن الرعاية الصحية لتخزين ونقل الغازات الطبية مثل الأكسجين والنيتروجين والهيليوم.
- اسطوانات مطفأة الحريق: تُستخدم أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم هذه في طفايات الحريق لتخزين الغازات المضغوطة مثل ثاني أكسيد الكربون أو النيتروجين.
- اسطوانات المشروبات: تُستخدم أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم هذه في صناعة المشروبات لتخزين وتوزيع ثاني أكسيد الكربون لكربنة المشروبات الغازية والبيرة وغيرها من المشروبات.
- اسطوانات الوقود البديلة: تخزن أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم هذه الغاز الطبيعي المضغوط (CNG) أو غاز البترول المسال (LPG) كوقود بديل في المركبات.
- اسطوانات الغاز المتخصصة: تُستخدم أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم لتخزين ونقل الغازات المتخصصة مثل غازات المعايرة والغازات النادرة والغازات عالية النقاء المستخدمة في البحث والتصنيع والتطبيقات المتخصصة الأخرى.
- اسطوانات التضخم والفضاء: تُستخدم أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم في صناعة الطيران لتضخيم منزلقات الطوارئ للطائرات ، والطوافات ، وسترات النجاة.
- اسطوانات سباق الأداء: تُستخدم أسطوانات الغاز المصنوعة من الألومنيوم في سباقات الأداء لتخزين وتوزيع أكسيد النيتروز لتعزيز المحرك.
- اسطوانات أخذ العينات: تُستخدم أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم هذه في المراقبة البيئية ، وتحليل الغاز ، والتطبيقات العلمية الأخرى لتخزين ونقل عينات الغاز للتحليل.
- اسطوانات أكسيد النيتروز: تستخدم أسطوانة غاز الألومنيوم لأكسيد النيتروز لتخزين ونقل غاز أكسيد النيتروز. أكسيد النيتروز هو غاز عديم اللون وذو رائحة حلوة يستخدم عادة كمخدر خفيف ومسكن للألم في الأوساط الطبية وطب الأسنان. كما أنها تستخدم في صناعة المواد الغذائية كمادة دافعة للكريمة المخفوقة وفي صناعة السيارات كمادة مضافة لتعزيز الأداء لمركبات السباق.
10. احتياطات السلامة لأسطوانة غاز الألومنيوم
فيما يلي بعض احتياطات السلامة الأساسية التي يجب اتخاذها عند التعامل مع أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم واستخدامها:
10.1 المناولة والتخزين المناسبين:
- احتفظ دائمًا بالأسطوانة في وضع مستقيم لمنعها من الانقلاب.
- استخدم عربة أو عربة مناسبة لتحريك الأسطوانة وتجنب سحبها على الأرض.
- قم بتأمين الأسطوانة بشكل صحيح عندما لا تكون قيد الاستخدام لمنعها من السقوط أو السقوط.
- لا ترفع الاسطوانة بواسطة الصمام أو المنظم.
10.2 الفحص الدوري والصيانة:
- اطلب فحص الأسطوانة بانتظام بواسطة فني مؤهل للتأكد من أنها في حالة جيدة.
- استبدل الأسطوانة إذا ظهرت عليها علامات التلف ، مثل الخدوش أو الشقوق أو التآكل.
- استبدل الصمام أو المنظم إذا كان تالفًا أو ظهرت عليه علامات التآكل.
10.3 تجنب التعرض لدرجات الحرارة القصوى:
- احتفظ بالأسطوانة بعيدًا عن مصادر الحرارة أو اللهب أو الشرر.
- لا تعرض الأسطوانة لدرجات حرارة أعلى من 130 درجة فهرنهايت (54 درجة مئوية) أو أقل من -40 درجة فهرنهايت (-40 درجة مئوية).
- قم بتخزين الأسطوانة في مكان بارد وجاف بعيدًا عن أشعة الشمس المباشرة.
باتباع احتياطات السلامة هذه ، يمكنك المساعدة في منع وقوع الحوادث وضمان التعامل الآمن مع أسطوانات غاز الألومنيوم واستخدامها.
11. الصين الصانع اسطوانة غاز الألومنيوم
إذا كنت بحاجة إلى أسطوانات غاز ألومنيوم عالية الجودة ، ففكر في الوصول إلى مصنع مرموق في الصين ، مثل Shining Aluminium Packaging. لدينا سجل حافل في إنتاج أسطوانات غاز الألمنيوم الموثوقة والمتينة لتطبيقات مختلفة.
لا تتردد في الاتصال بنا للحصول على مزيد من المعلومات أو لطلب عرض أسعار. بفضل خبرتهم والتزامهم بالجودة، يمكننا أن نقدم لك الحلول المناسبة لاحتياجاتك الخاصة.
12. التعليمات
تستخدم اسطوانات الألمنيوم لتخزين ونقل الغازات المضغوطة مثل الأكسجين والنيتروجين وثاني أكسيد الكربون. غالبًا ما تستخدم في البيئات الصناعية والطبية والمخبرية.
يجب أن تلبي أسطوانات الألمنيوم معايير السلامة الصارمة وأن يتم فحصها واختبارها بانتظام. ابحث عن العلامات الموجودة على الأسطوانة التي تشير إلى أنه قد تم اختبارها واعتمادها ، وتحقق من تاريخ انتهاء الصلاحية للتأكد من أنها لا تزال في فترة خدمتها.
يجب تخزين أسطوانات الألمنيوم في مكان بارد وجاف وجيد التهوية بعيدًا عن مصادر الحرارة أو اللهب أو الاشتعال. يجب تخزينها بشكل عمودي وتأمينها في وضع ثابت لمنع السقوط.
نعم، يمكن إعادة تعبئة أسطوانات الألمنيوم بالغاز المناسب أو خليط الغازات طالما تم اختبارها واعتمادها بشكل مناسب. اتبع دائمًا تعليمات الشركة المصنعة واستخدم معدات التعبئة المناسبة.
يجب نقل أسطوانات الألمنيوم في وضع مستقيم وآمن ومؤمن لمنعها من التحرك أو السقوط أثناء النقل. بالإضافة إلى ذلك ، يجب نقلها في منطقة جيدة التهوية وبعيدًا عن مصادر الحرارة أو اللهب أو الاشتعال.
نعم ، يمكن إعادة تدوير أسطوانات الألمنيوم. تحقق من مرفق إعادة التدوير المحلي الخاص بك لمعرفة كيفية التخلص من أسطوانة الألمنيوم الخاصة بك بشكل صحيح.
يمكن أن تكون أسطوانات الألمنيوم خطرة إذا لم يتم التعامل معها بشكل صحيح. قد تنفجر إذا تعرضت للحرارة العالية أو اللهب أو في حالة تلفها أو تلفها. اتبع دائمًا إجراءات السلامة المناسبة عند التعامل مع أسطوانات الألمنيوم ، واطلب العناية الطبية على الفور في حالة التعرض لغاز مضغوط أو تلف أسطوانة الألمنيوم.
يمكن أن يشير مقياس الضغط الموجود على صمام الأسطوانة إلى كمية الغاز المتبقية هناك. ومع ذلك، من المهم ملاحظة أن مقياس الضغط يظهر فقط ضغط الغاز، وليس كمية الغاز المتبقية في الأسطوانة. لذلك، لتحديد كمية الغاز المتبقية بدقة، قد تحتاج إلى وزن الاسطوانة.
يمكن استخدام أسطوانات الألمنيوم للغطس تحت الماء ، ولكن يجب أن تكون مصممة خصيصًا ومعتمدة. يجب أيضًا ملؤها بخليط الغاز المناسب للغوص ، مثل الهواء أو النيتروكس أو التريميكس.
في حالة تلف أسطوانة الألمنيوم أو تسريبها ، يجب إزالتها على الفور من الخدمة ونقلها إلى منشأة فحص الأسطوانة المؤهلة للفحص والإصلاح. لا تحاول إصلاح أو استخدام أسطوانة تالفة.
يمكن طلاء أو طلاء أسطوانات الألمنيوم، لكن من الضروري استخدام الطلاء أو الطلاء المناسب المتوافق مع الغاز المخزن في الأسطوانة. استشر الشركة المصنعة أو مفتش الأسطوانة المؤهل للحصول على التوصيات.
يجب فحص واختبار أسطوانات الألمنيوم على فترات منتظمة، كما هو محدد من قبل الشركة المصنعة والهيئات التنظيمية. يتضمن هذا عادةً فحصًا بصريًا واختبارًا هيدروستاتيكيًا، والذي يختبر قدرة الأسطوانة على تحمل الضغط بأمان. تختلف فترات الفحص والاختبار حسب نوع الأسطوانة والاستخدام المقصود منها.
يمكن استخدام أسطوانات الألومنيوم لتخزين الغازات الغذائية ، مثل ثاني أكسيد الكربون ، لكربنة المشروبات. ومع ذلك ، يجب تصميم الأسطوانة واعتمادها خصيصًا لهذا الاستخدام ، ويجب أن يكون الغاز معتمدًا على أنه من الدرجة الغذائية.
يمكن استخدام أسطوانات الألمنيوم لتخزين الأكسجين الطبي ، ولكن يجب تصميمها واعتمادها لهذا الاستخدام. بالإضافة إلى ذلك ، يجب تنظيف الأسطوانة وتعقيمها قبل استخدامها لمنع التلوث.
لا ينصح باستخدام أسطوانات الألومنيوم لتخزين الغازات المسببة للتآكل ، حيث يمكن أن يتفاعل الألمنيوم مع بعض الغازات المسببة للتآكل ويتسبب في جعل الأسطوانة غير مستقرة أو حتى تنفجر. بدلاً من ذلك ، استشر الشركة المصنعة أو مفتش أسطوانة مؤهل للحصول على توصيات بشأن مادة الأسطوانة المناسبة لتخزين الغازات المسببة للتآكل.