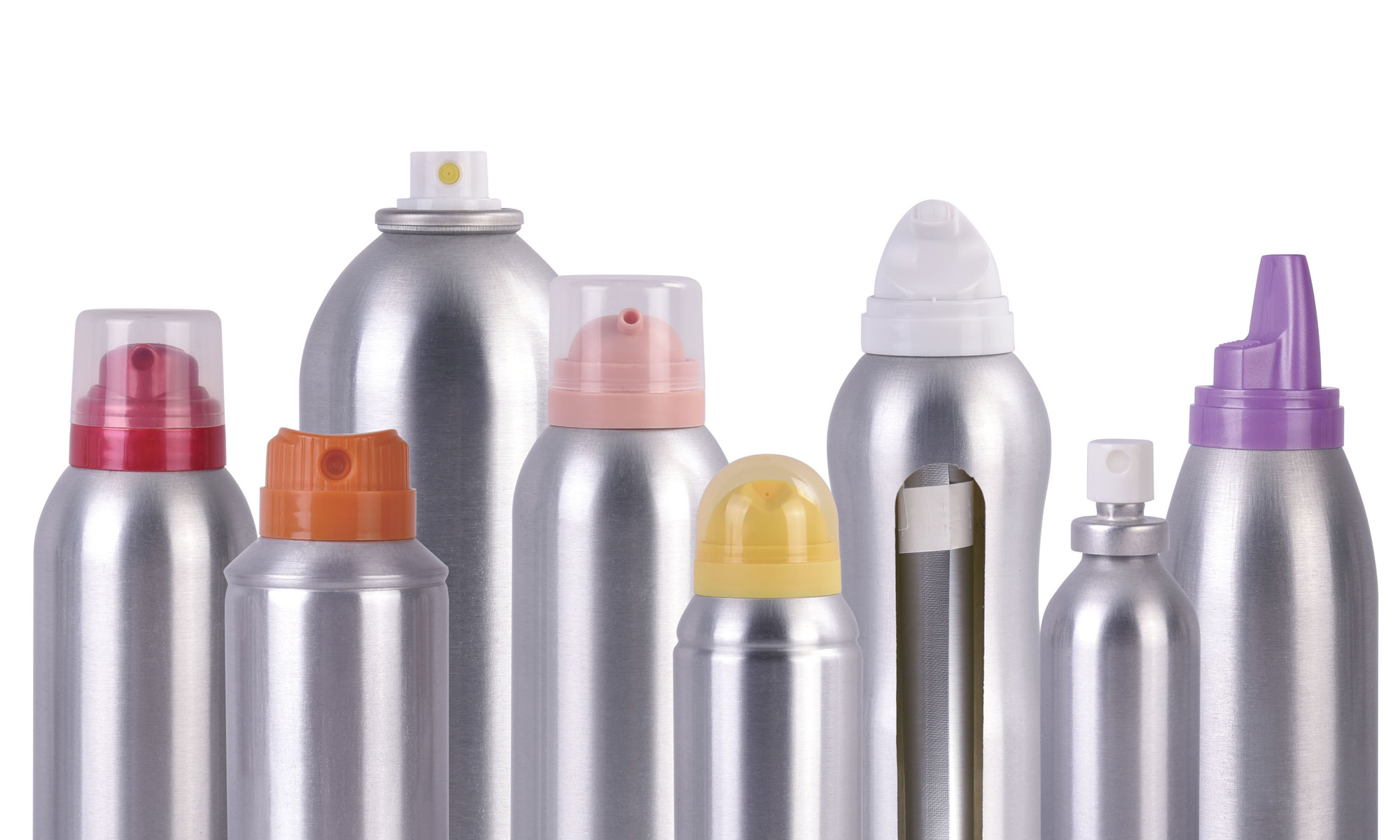
Introducción a la terminología de las válvulas de aerosol y recursos de la industria
En el mundo de Fabricación de válvulas de aerosolTener una comprensión clara de la terminología esencial y los recursos disponibles puede marcar una gran diferencia. Las válvulas de aerosol son sistemas complejos que se utilizan en distintas industrias, desde la cosmética hasta la alimentación y la automoción, y requieren una ingeniería precisa para cumplir con los estándares regulatorios y las expectativas de los consumidores. Esta guía sirve como una referencia completa para fabricantes y proveedores por igual, y detalla términos y recursos clave para capacitar a los profesionales en la selección, el diseño y la optimización de válvulas de aerosol para sus productos.
Por qué es importante que los fabricantes comprendan los términos de las válvulas de aerosol
Comprender los componentes y las funciones específicas de las válvulas de aerosol es fundamental en la producción. Conocer estos términos ayuda a los fabricantes a garantizar la calidad, la funcionalidad y la seguridad de sus productos. Este glosario cubre términos que van desde los tipos de actuadores hasta los sistemas de propulsión, lo que brinda a los fabricantes experimentados y nuevos una ventaja en el control de calidad y la innovación.
Glosario de términos clave en válvulas de aerosol
1. Solenoide
El actuador es la parte de la válvula que el usuario presiona para liberar el producto. Los actuadores vienen en varios diseños, cada uno de los cuales influye en la velocidad, el patrón y el flujo de rociado. En las versiones de ruptura mecánica (MBU) y de ruptura no mecánica (no MBU), los actuadores están diseñados para aplicaciones que van desde nieblas finas hasta rociados dirigidos. Los diferentes diseños de actuadores pueden afectar directamente el rendimiento del producto, especialmente en aplicaciones como desodorantes e insecticidas donde los patrones de rociado consistentes son vitales.
2. Propulsor
Los propulsores son gases, a menudo licuados o comprimidos, que crean presión en las latas de aerosol. Los tipos más comunes incluyen hidrocarburos, nitrógeno y dióxido de carbono. La elección del propulsor afecta el diseño y la aplicación de la válvula. Por ejemplo, los hidrocarburos ofrecen alta presión pero conllevan consideraciones ambientales, mientras que el nitrógeno es una opción no inflamable y respetuosa con el medio ambiente.
3. Tubo de inmersion
Un tubo de inmersión se extiende desde la válvula hasta el producto, lo que permite que el líquido se aspire y se pulverice. La longitud y el material adecuados del tubo de inmersión son cruciales para lograr una calidad de pulverización uniforme, especialmente en productos de alta viscosidad o que forman espuma. La mayoría de los tubos de inmersión están diseñados para maximizar la evacuación del producto sin obstrucciones.
4. Copa de válvula
La copa de la válvula fija la válvula a la lata y proporciona el punto de conexión para el actuador. Se eligen diferentes materiales (acero estañado, aluminio) en función de la compatibilidad del producto, ya que la copa de la válvula debe soportar presiones internas sin comprometer la integridad del producto.
5. Engarce
El engarce es el proceso de unir la válvula a la lata, asegurando un sellado hermético para evitar fugas. Este es un procedimiento de precisión, que a menudo requiere equipo especializado y controles de calidad estrictos para garantizar un sellado confiable. Un engarce desalineado o incorrecto puede provocar fallas en la válvula y fugas de producto.
6. Provenir
El vástago canaliza el producto desde el tubo de inmersión hasta el actuador, controlando el caudal. Los vástagos, que suelen estar hechos de plástico, vienen con orificios de distintos tamaños para controlar el caudal y las características de pulverización, lo que es especialmente importante para aplicaciones especializadas como aerosoles industriales o de grado alimenticio.
7. Junta de sellado
La junta de estanqueidad es el componente que garantiza el sellado hermético de la válvula cuando no se utiliza. Se utilizan diferentes formulaciones, como neopreno o caucho butílico, en función de la composición química del producto en aerosol, lo que evita fugas y garantiza la estabilidad del producto a lo largo del tiempo.
8. Llenado a presión
El llenado a presión es un método en el que el producto se llena bajo presión para garantizar que el envase se llene por completo. Este método se utiliza habitualmente en aplicaciones que requieren una liberación rápida del producto y un alto rendimiento, como se observa en los aerosoles de limpieza y los ambientadores.
9. Sistema de bolsa con válvula (BOV)
En un sistema de bolsa con válvula, el producto se almacena en una bolsa dentro de la lata, separado del propelente. Esto garantiza que no haya contacto entre el propelente y el producto, lo que resulta ideal para formulaciones sensibles como los cosméticos o los productos farmacéuticos.
10. Patrón de rociado
El patrón de rociado es la forma y la consistencia del producto a medida que se dispensa. Los patrones pueden variar desde chorros estrechos hasta nieblas amplias, cada uno adecuado para aplicaciones específicas, como aerosoles corporales o lubricantes industriales. Ajustar el actuador o el orificio puede optimizar el patrón para diferentes usos.
Recursos clave de la industria para fabricantes de válvulas de aerosol
Para los fabricantes, es fundamental mantenerse informados sobre las normas y directrices más recientes. A continuación, se indican algunos recursos y organizaciones importantes:
- Asociación de productos especiales para el consumidor (CSPA):Proporciona estándares industriales y recursos técnicos, particularmente para el cumplimiento de las normas ambientales y de seguridad. Sitio web de la CSPA.
- Federación Europea de Aerosoles (FEA):Establece estándares europeos para la fabricación de aerosoles, cruciales para los proveedores que operan a nivel internacional. Sitio web de la FEA.
- Asociación Nacional de Aerosoles (NAA)Organización con sede en EE. UU. que ofrece pautas, noticias de la industria y soporte técnico para fabricantes de aerosoles. Sitio web de la NAA.
- Administración de Seguridad y Salud Ocupacional (OSHA):Garantiza condiciones de trabajo seguras y ofrece directrices sobre el manejo de propelentes y sustancias peligrosas. Sitio web de OSHA.
Preguntas frecuentes: válvulas de aerosol
Para ayudar a los fabricantes y proveedores, aquí encontrará respuestas a algunas preguntas frecuentes:
- ¿Cuál es el mejor propulsor para aplicaciones respetuosas con el medio ambiente? Los gases comprimidos como el nitrógeno y el dióxido de carbono son buenas opciones para productos ecológicos.
- ¿Cómo puedo garantizar un patrón de pulverización uniforme? Utilice actuadores con tecnología MBU para lograr pulverizaciones finas y consistentes.
- ¿Cuál es la importancia del crimpeado? Un engarzado adecuado garantiza un sellado hermético, evitando fugas y manteniendo la calidad del producto.
- ¿Cómo selecciono la longitud correcta del tubo de inmersión? El tubo de inmersión debe llegar hasta el fondo de la lata para garantizar la evacuación completa del producto.
- ¿Puedo utilizar la misma válvula para diferentes viscosidades de producto? No, seleccione válvulas y vástagos adecuados a la viscosidad específica para un control de flujo óptimo.
- ¿Cuál es el papel de una junta de estanqueidad? Las juntas evitan fugas y garantizan la estabilidad del producto manteniendo un sello hermético.
- ¿Existen requisitos reglamentarios para las válvulas de aerosol? Sí, el cumplimiento de las normas de organismos como OSHA y FEA es esencial.
- ¿Para qué se utiliza un sistema Bag-on-Valve? Los sistemas BOV son ideales para formulaciones sensibles que requieren separación del propulsor.
- ¿Cómo puedo controlar la velocidad de pulverización? Ajuste el tamaño de los orificios del vástago o utilice modificaciones del actuador para controlar las tasas de pulverización.
- ¿Dónde puedo encontrar más recursos sobre la tecnología de válvulas de aerosol? Organizaciones como CSPA, FEA y NAA proporcionan valiosos recursos técnicos.
Conclusión
Un conocimiento profundo de la terminología y los recursos de las válvulas de aerosol proporciona a los fabricantes el conocimiento necesario para crear productos más seguros y de alta calidad. Para obtener más información, Contáctenos directamente o visitar Nuestra página de válvulas de aerosol Para conocer las últimas ofertas y actualizaciones de productos. ¡Trabajemos juntos para mejorar sus soluciones de aerosoles!