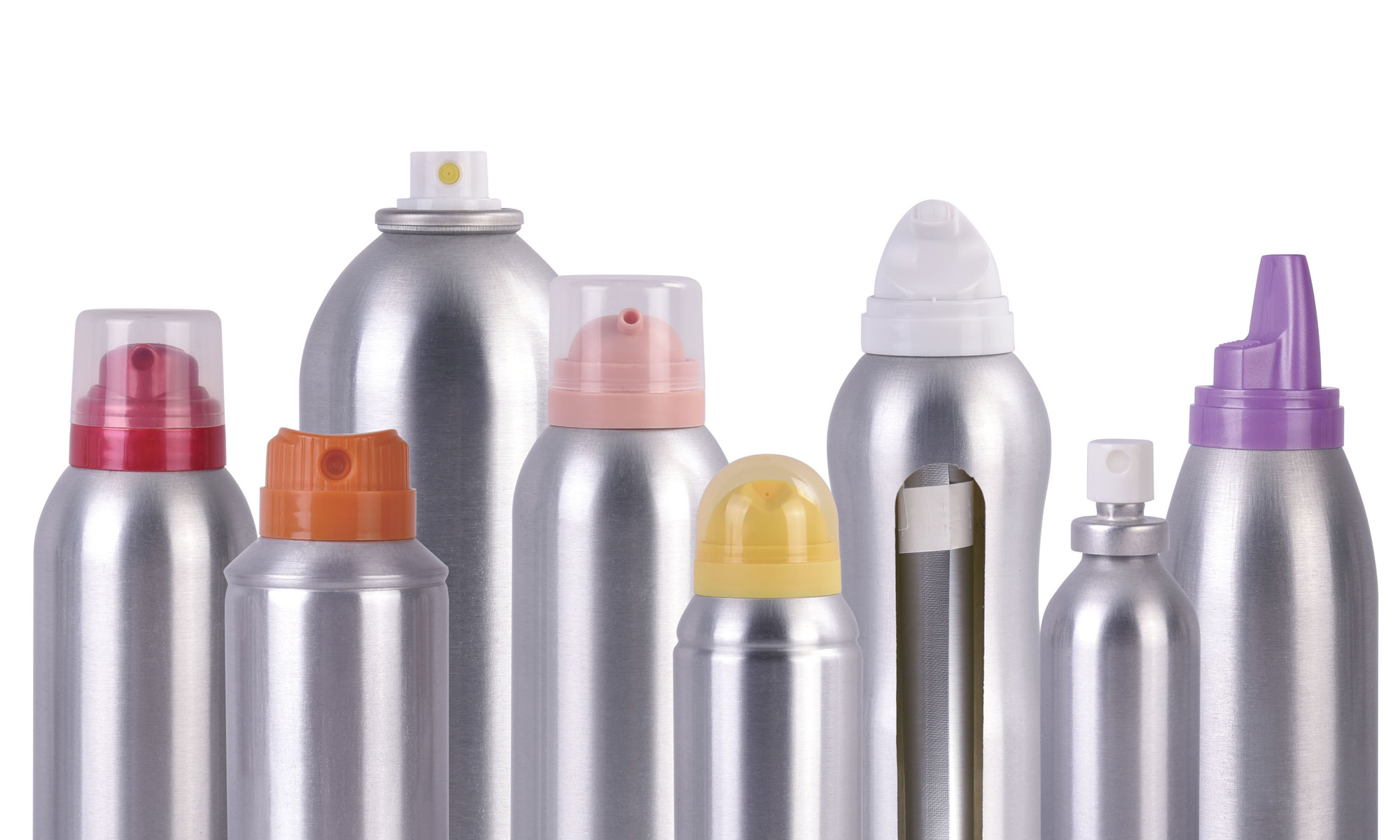
Introduction
Les propulseurs jouent un rôle essentiel dans la fonctionnalité et l’efficacité des valves d'aérosol, garantissant un débit de produit constant, des modèles de pulvérisation contrôlés et des performances fiables dans le temps. Le choix du bon type de propulseur est essentiel non seulement pour obtenir les résultats souhaités du produit, mais également pour maintenir les normes de sécurité et minimiser l'impact environnemental. Dans cet article, nous examinons les principaux types de propulseurs utilisés dans les valves d'aérosol, les facteurs de sélection et les conseils que les fabricants doivent prendre en compte pour des résultats optimaux.
Aperçu des types de propulseurs : gaz liquéfiés et gaz comprimés
Dans le monde de valves d'aérosolLes propulseurs se répartissent généralement en deux catégories : les gaz liquéfiés et les gaz comprimés. Ces deux types diffèrent en termes de pression, de consistance et de considérations environnementales.
1. Gaz liquéfiés
Les gaz liquéfiés sont largement utilisés comme propulseurs en raison de leur capacité à maintenir une pression constante dans le récipient. Les hydrocarbures tels que le propane, le butane et l'isobutane en sont des exemples courants. Sous pression, ces gaz restent à l'état liquide mais se transforment rapidement en gaz lorsqu'ils sont libérés par la valve aérosol, offrant ainsi une pulvérisation constante. En raison de la constance de leur pression, les gaz liquéfiés sont souvent préférés dans les applications où un jet uniforme est essentiel, comme dans les produits de soins personnels.
2. Gaz comprimés
Gaz comprimés, y compris le dioxyde de carbone (CO2), azote (N2) et l'oxyde nitreux (N2Les propulseurs O) fonctionnent en occupant uniquement l'espace libre du récipient, ce qui signifie qu'ils appliquent la pression uniquement à partir de la phase gazeuse. Contrairement aux gaz liquéfiés, ces propulseurs perdent de la pression au fur et à mesure de l'utilisation du produit, ce qui peut entraîner une pulvérisation irrégulière vers la fin de l'utilisation de la bombe. Les gaz comprimés sont préférés pour les produits qui ne nécessitent pas un jet constant ou pour les formulations sensibles aux hydrocarbures.
Sélection des propulseurs : critères clés de performance, de sécurité et d'impact environnemental
Le choix du type de propulseur approprié nécessite un équilibre entre performances, sécurité et impact environnemental. Chaque application peut avoir des exigences uniques, mais il existe des directives générales à suivre.
Considérations relatives aux performances
Le propulseur doit être compatible avec la formulation et le système de valve pour assurer une pulvérisation efficace. Les gaz liquéfiés, par exemple, sont souvent plus efficaces avec les produits nécessitant une pulvérisation continue, tandis que les gaz comprimés peuvent être plus adaptés aux produits utilisés en rafales.
Normes de sécurité
La sécurité est primordiale, en particulier pour les produits de grande consommation. Les gaz liquéfiés inflammables comme le propane et le butane doivent être stockés avec précaution et nécessitent souvent un étiquetage et une manipulation spéciaux. En revanche, les gaz comprimés non inflammables comme l'azote offrent une option plus sûre pour les produits utilisés dans des environnements sensibles.
Préoccupations environnementales et réglementaires
Ces dernières années, l'industrie des aérosols s'est orientée vers des choix respectueux de l'environnement. Les gaz liquéfiés à base d'hydrocarbures contribuent aux composés organiques volatils (COV), qui sont réglementés dans de nombreuses régions. Les gaz comprimés comme l'azote, le CO2, et le protoxyde d’azote offrent des alternatives avec un impact environnemental moindre, ce qui les rend idéales pour les produits respectueux de l’environnement.
Minimiser l’impact environnemental grâce à des options de propulseurs durables
Pour les fabricants soucieux de la durabilité, la réduction des émissions de COV est une préoccupation majeure. Voici quelques stratégies pour utiliser des propulseurs plus durables :
- Air comprimé : Option respectueuse de l’environnement, l’air comprimé fournit un propulseur ininflammable et sûr qui ne contribue pas aux COV.
- CO2 et le protoxyde d'azote : Les deux CO2 et N2O ont un faible impact environnemental. Cependant, il est essentiel de surveiller leur interaction avec la formule du produit, car le CO2 peut altérer la saveur ou provoquer la formation de mousse dans certains produits.
- Mélanges de gaz comprimés et liquéfiés : Les fabricants peuvent combiner les avantages des deux types de propulseurs pour obtenir des caractéristiques de performance spécifiques tout en réduisant les émissions de COV.
Conseils pratiques pour les fabricants
Lorsque vous évaluez les options de propulseur, gardez à l’esprit les conseils suivants pour garantir des performances optimales et l’intégrité du produit :
- Effectuer des tests de compatibilité rigoureux : Assurez-vous que le propulseur choisi ne réagit pas négativement avec la formulation ou les composants de la valve.
- Évaluer les besoins en pression : Chaque produit aérosol peut avoir des besoins de pression uniques en fonction de son application, adaptez donc le choix du propulseur en conséquence.
- Tenir compte des réglementations géographiques : Les réglementations sur les propulseurs varient d'un pays à l'autre. Par exemple, certaines régions imposent des restrictions sur les émissions de COV qui peuvent affecter le choix du propulseur.
10 questions courantes sur les propulseurs à valve d'aérosol
- Quelle est la différence entre le gaz liquéfié et le gaz comprimé comme propulseur ? Les gaz liquéfiés fournissent une pulvérisation constante et maintiennent la pression, tandis que les gaz comprimés offrent des pulvérisations intermittentes avec une diminution progressive de la pression.
- Tous les gaz liquéfiés sont-ils inflammables ? La plupart sont inflammables, comme le propane et le butane, mais certaines exceptions existent, comme l’éther diméthylique (DME) lorsqu’il est utilisé avec prudence.
- Peut-CO2 être utilisé dans les valves d'aérosols de qualité alimentaire ? Oui, CO2 est couramment utilisé dans les produits alimentaires comme la crème fouettée, mais il nécessite une compatibilité de valve spécifique.
- Quels sont les impacts environnementaux des propulseurs d’aérosols ? Les hydrocarbures contribuent aux émissions de COV, tandis que les gaz comprimés comme le N2 et CO2 avoir un impact environnemental moindre.
- L’azote est-il une alternative viable aux hydrocarbures traditionnels ? Oui, l’azote est une option sûre, non inflammable et écologique, mais peut ne pas convenir à tous les produits nécessitant une pulvérisation continue.
- Comment choisir un propulseur pour les produits à haute viscosité ? Les produits à haute viscosité nécessitent souvent des gaz liquéfiés pour un meilleur maintien de la pression et une pulvérisation uniforme.
- Existe-t-il des propulseurs écologiques pour les produits cosmétiques ? Air comprimé, azote et CO2 sont d’excellents choix pour les applications cosmétiques respectueuses de l’environnement.
- Que doivent prendre en compte les fabricants en matière de sécurité des propulseurs ? L’inflammabilité, la toxicité et le stockage approprié doivent être évalués pour garantir la sécurité de l’utilisateur et de l’environnement.
- Pourquoi certains propulseurs sont-ils restreints dans certaines régions ? Les réglementations sur les COV et les préoccupations environnementales imposent souvent des restrictions d’utilisation des propulseurs en fonction de la situation géographique.
- Comment puis-je trouver plus d’informations sur les options de valves aérosols ? Visite notre site ou des sources fiables comme Article de Wikipédia sur les aérosols pour plus de détails.
Conclusion
La sélection du propulseur adapté à vos valves d'aérosol nécessite une compréhension complète des besoins de performance, des normes de sécurité et des considérations environnementales. En évaluant soigneusement chaque type et en consultant des experts, les fabricants peuvent améliorer l'efficacité de leurs produits tout en respectant les normes réglementaires. Pour plus d'informations ou pour découvrir nos options de valves d'aérosol, contactez notre équipe ou visitez notre page produit aujourd'hui!